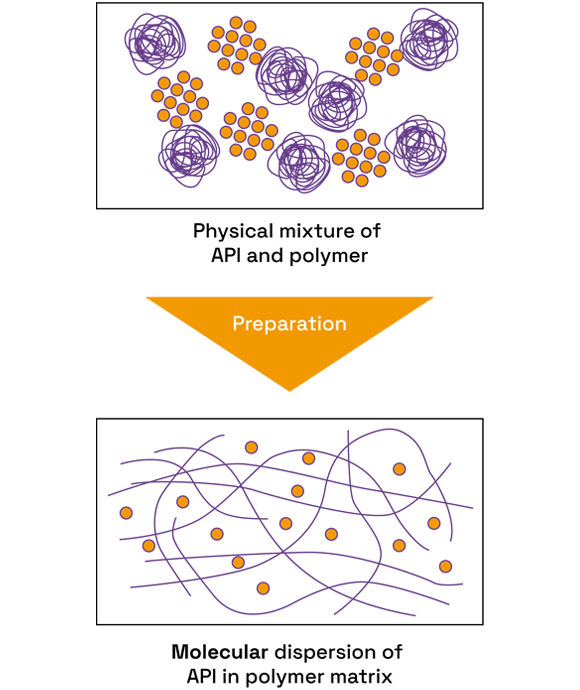
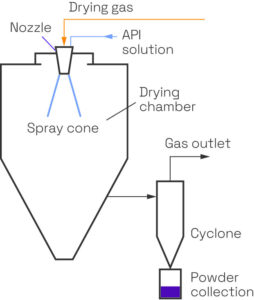
We offer comprehensive amorphous solid dispersion (ASD) services, using small quantities of material, in order to help customers improve the solubility and bioavailability of pharmaceutical compounds.
- Increase the apparent solubility of the API and maximize bioavailability
- Accelerate drug development by helping to select the right drug candidate at an early stage
- Provide an alternative approach to enhancing bioavailability
- Maximize the chances of creating a successful new drug product
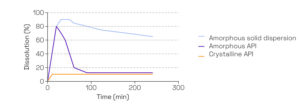
- Understand and maximize dissolution behavior to help predict in vivo behavior
- Generate IP
- Extend the life of a product or patent and help develop new generations of a drug
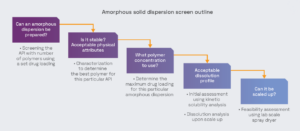
Performing amorphous solid dispersion studies, in parallel with our other solid state services, enables effective candidate selection at an early stage, increasing the chances of successful development.